Microsoft Excel 2007 - Workbooks and worksheets
Workbook
A spreadsheet document (or file) is called a workbook. This means that when we refer to Saving a file, we are in fact saving the workbook. It is just a matter of a name. A workbook is a document and it is a file that gets saved to disk. Initially, a workbook is labelled Book1 or Book2 etc (see the Title bar in the image below), until you save it and give a name of your own.
When you open a workbook you will see a page filled with rows and columns.
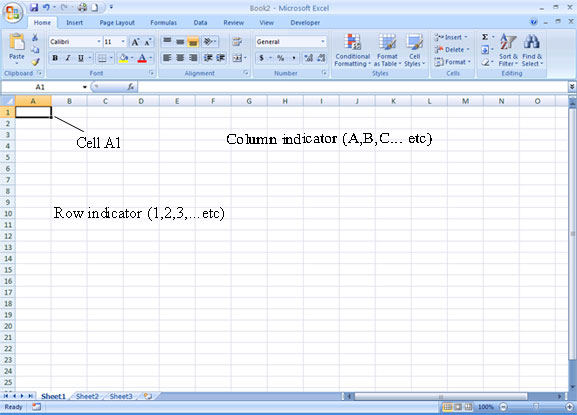
Rows are labelled
with numbers. There are 1 048 576 rows.
Columns are labelled with letters of the
alphabet. There are 16 384 columns.
A Cell is identified by its row and column indicators. In the image below Cell A1 is in Column A and Row 1. We normally enter one piece of data in a cell.
When you open a new workbook, you
will see that it is not only a big sheet of many rows and
columns, but that it contains 3 worksheets (sheet 1, sheet 2, sheet 3). Each worksheet contains
1 048 576 rows and 16 384 columns.
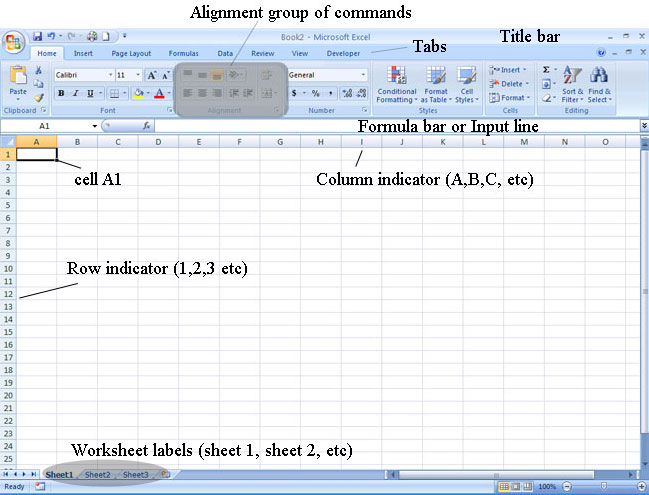
The Worksheets are labelled Sheet1, Sheet2 and Sheet3, until you rename them. Normally you only use one worksheet however you could use different worksheets, for instance, if you want to keep all your class's record of marks over the year in one workbook, You would then rename the sheets according to the classes e.g. Grade 8B, Grade 9A etc.
Click on the Sheet tab at the bottom the page (circled above). Then...
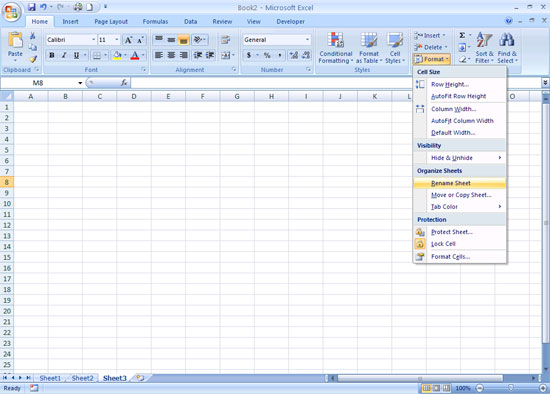
Click on Format in the cells
group at the top of the screen
Click on Rename
Sheet
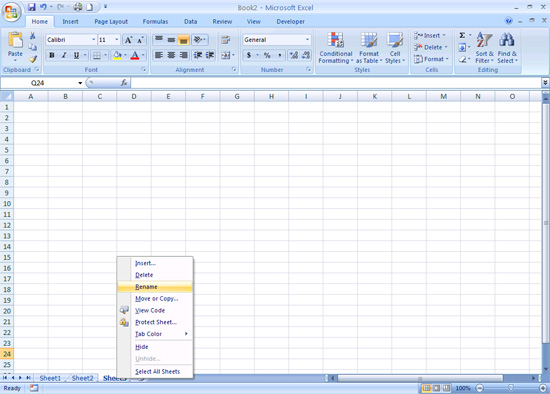
Alternatively
Right Click the
Sheet
tab
Click on Rename
When to use a workbook and when to use a worksheet
The following extract comes from www.ehow.com
A "workbook" is a Microsoft Excel file. Each workbook can hold many "worksheets" (individual spreadsheets). Use multiple worksheets to group related data. For example, you might have a sheet for each quarter's detailed budget, plus a sheet for a streamlined version of the yearly budget. You can reference cells in other sheets: your yearly budget, for example, could reference data from the quarterly sheets.
Tips
- Use multiple worksheets when creating spreadsheets for several related groups of information.
- Don't use multiple worksheets if your spreadsheets aren't related - create a new workbook instead.
- Don't use multiple worksheets to create "what if" scenarios for the same group of information (for example, best case, worst case, and most likely scenarios for one budget); use the What-if Analysis command on the Data tab.
- To go to a new worksheet, click its tab at the bottom of the spreadsheet window.
- To use data from one worksheet in another worksheet's formula, just select the cells you want to refer to and paste them in the formula as you would other cells.
- If sheets in your workbook will use similar formatting, you can create the first sheet, then save it as a template and use it as the basis for subsequent sheets. (Use the Save As command in the File menu to save the worksheet as a template.)
All Rights Reserved.